How to Manage Insulin Resistance: What You Need to Know
by Erika Slater
You may hear the term Insulin resistance (IR) before but are not sure you fully understand why it happens and what you can do about it. It is a medical diagnosis that can have far-reaching consequences. One of the first questions people with IR have when diagnosed is how to fix and manage their insulin resistance.
Before tackling that questions, I need to talk some basics with you.
What is insulin? Insulin is produced in the pancreas. The primary function of insulin is to allow your body to use sugar produced from carbohydrates (carbs), also known as glucose. When you eat carbs, you are eating foods rich in glucose which are sugars. Sugars are used for energy. Insulin is like an ‘energy stabilizer’ for your energy stores. Insulin facilitates that energy is used appropriately and distributed at proper levels.
Insulin resistance is a condition wherein the body’s response to insulin becomes inadequate, resulting in heightened glucose concentrations within the bloodstream. This increased glucose level can cause numerous complications if left untreated, including heart disease and diabetes. But with proper diagnosis and treatment, many people can successfully manage their insulin resistance while preventing further health issues.
Many of the clients I see are for weight loss and sugar addiction. To help my clients better understand their eating habits and how they impact their health and weight, I began researching insulin resistance when I started offering these services in 2004. Today we know much more about the topic, and it is time to update my resources. So, together with expanded information on IR and contributions from my colleague Dr. Peter Sacco – I have compiled this blog post as a resource for my weight loss and sugar addiction clients and for anybody else looking to understand how insulin works and what happens when it no longer performs its role effectively for our body.
In this blog post, I’ll explore what exactly insulin resistance is, how it’s diagnosed and treated, its potential complications, and how to manage IR from a daily perspective—all so you can make an informed decision about your health.
Table of Contents:
- What is Insulin Resistance?
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Insulin Resistance
- Complications of Untreated Insulin Resistance
- Prevention of Insulin Resistance
- Summary and Resources for Further Information on Insulin Resistance
- FAQs in Relation to Insulin Resistance
- How to Manage Insulin Resistance Final Points
What is Insulin Resistance?
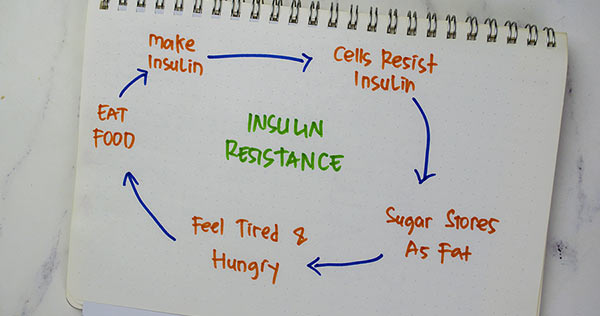
The human body is a sophisticated machinery operating like an automobile. Just as you need gasoline to run an automobile (these days, more cars are using other energy-efficient methods as well), you need the energy to make your body operate, in this case, sugar. In automobiles, you pour the gasoline into the gas tank, but it has to go through a process before it makes the engine run effectively. The same happens when you put sugar into your body (carbohydrates). The sugar does not go directly into your cells; it must be processed and converted.
The process is quite simple! Your blood sugar levels will rise whenever you eat your meal, signaling your brain to release insulin into your bloodstream through the pancreas. These cells are known as ‘beta cells.’ Perhaps the best way to describe insulin in this process is to look at it as a ‘key.’ It works to unlock your cells, thus causing them to allow ‘sugar’ to enter the cells so that they can be used for energy to burn for the sustenance and maintenance of the body. In a nutshell, insulin is the key for signaling cells and then attaching to them to absorb sugar into your bloodstream.
Whenever you have more sugar than your body needs (you’ve consumed too much, for example), insulin serves as a ‘facilitator’ and tells your brain to store the excess sugar in your liver or other areas and re-release it into your bloodstream, whenever your blood sugar levels are low. When you engage in physical activity, your body needs more energy, and the sugar is released into your bloodstream for fuel. The same process happens in between meals to sustain you. Your insulin works to keep your blood sugar in a normal range, always seeking to keep it in balance.
Insulin resistance (IR) is when the body’s cells do not respond normally to insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. Insulin helps manage your blood sugar levels and facilitates glucose to enter cells where it can be used for energy. Glucose access to cells is impaired when IR arises, thus prompting a rise in blood sugar levels.
Insulin insensitivity occurs when body cells become less responsive to insulin’s effects. This means that your body must produce more and more insulin to maintain blood sugar levels within the normal range.
The precise cause of IR is still unclear. Still, many possibilities could be at play, such as heredity, obesity, lack of physical exertion, advanced age, specific drugs, and hormones like cortisol or somatotropin. It has been suggested that IR might be associated with sustained inflammation caused by conditions like arthritis or illnesses including HIV/AIDS.
Insulin resistance can lead to significant health repercussions. Through careful diagnosis and treatment, however, it can be managed to help improve overall health. Now let’s look at how we can diagnose and treat insulin resistance.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Insulin Resistance
Diagnosing and managing IR can help avoid serious health issues like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, stroke, and metabolic syndrome.
To diagnose IR, your doctor may require a fasting glucose assessment or an oral glucose tolerance test to evaluate how well your body is processing sugar after consuming carbohydrates. Your physician could also request additional checks, for example, a hemoglobin A1C test to assess average glucose levels in the long run or an insulin level assessment to inspect for excessive quantities of insulin in the bloodstream.
Treatment approaches for insulin resistance may differ depending on personal considerations but usually involve changes in diet and eating habits and increased physical activity such as exercise. In some cases, your primary care physician may combine habit changes with drugs such as metformin which can help decrease insulin resistance by improving sensitivity to existing insulin. Always ask the prescriber about side effects and issues with any other medications you may be taking when taking a drug. Know that a pill is no substitute for a healthy lifestyle. When taking medicine where possible, you should still eat healthily and exercise. As changes occur over time, you may be able to reduce or stop taking medications with your doctor’s direction.
Consuming a nutritious diet abundant in fruits, veggies, whole grains, lean proteins, and beneficial fats can help manage insulin resistance by maintaining blood sugar levels while diminishing inflammation. Regular exercise helps increase muscle mass, increasing sensitivity to the available insulin, so getting at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity most days of the week, if possible, is recommended. Additionally, limiting alcohol consumption and quitting smoking is beneficial since both activities have been linked with increased risk for developing IR in individuals.
If you experience challenges eating healthy foods or find yourself in the evening snacking, eating comfort foods, or lacking the motivation to exercise regularly, consider working with a hypnotherapist, personal trainer, or coach to monitor and help you achieve these necessary lifestyle changes.
Proper diagnosis and treatment of insulin resistance can help reduce the risk of developing serious health complications, so it’s important to take steps to understand your risks and get proper medical care. In the next section, I’ll discuss the probable perils that may arise from ignoring the signs of insulin resistance.
Complications of Untreated Insulin Resistance
Untreated insulin resistance can lead to several serious health complications. Cardiovascular disease is one of untreated IR’s most common and dangerous risks. Possible complications include hypertension, hardened arteries, and a heightened possibility of stroke or cardiac arrest. Untreated insulin resistance may also lead to higher LDL cholesterol (the ‘unfavorable’ type) and lower HDL cholesterol levels (the ‘advantageous’ kind).
Metabolic syndrome can also be an associated complication if left untreated. Metabolic syndrome is a constellation of indicators comprising obesity, raised triglycerides, low HDL cholesterol, hypertension, and high fasting glucose levels. Having metabolic syndrome increases the likelihood of type 2 diabetes and other cardiovascular issues like coronary artery disease and stroke.
Several potential health complications that can appear when insulin resistance is not addressed include issues such as fatty liver disease, sleep apnea, depression or anxiety disorders, some forms of cancer like colorectal and breast (in postmenopausal women), acanthosis nigricans skin conditions; kidney damage; vision problems; nerve harm causing numbness/tingling in hands/feet; infertility for both genders; and gouty arthritis from uric acid build-up due to glucose metabolism.
If you suspect that you may have insulin resistance consult your doctor so you can be evaluated further and they can discuss with you appropriate treatment options. Treatment will be based on individual needs and lifestyle factors.
Left unaddressed, insulin resistance can lead to a host of medical issues. Fortunately, there are steps that can be taken to impede or stop the occurrence of insulin resistance. Let’s delve deeper into these preventive approaches.
Prevention of Insulin Resistance
Maintaining a healthy eating pattern and active lifestyle is the most effective way to prevent insulin resistance. Eating foods low in carbohydrates, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and a diet low in saturated fats, can help manage blood sugar levels. Limiting processed foods and added sugars can also benefit those at risk of developing insulin resistance. Additionally, regular physical activity helps improve glucose metabolism by increasing muscle mass. Adults should aim to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise each week, coupled with strength training.
Omega-3s, chromium, magnesium, zinc, ALA (alpha lipoic acid), D3, and curcumin from turmeric root powder have all been explored for their capability to reduce the onset of insulin resistance. Despite some investigations proposing that these supplements may be advantageous when taken with a nutritious diet and frequent physical activity, more research is required to draw definitive conclusions regarding their effectiveness.
In my experience working with weight loss clients, difficulty keeping on a healthy diet and exercise regime is usually complicated by emotional stress. Adults generally know what foods are good and bad these days. There is truth in the “protein and veg” diet as a mantra. But knowing doesn’t necessarily mean adhering. If you find yourself reaching for comfort foods or snacks regularly and fighting to stay on a healthy diet, you may need to find additional professional help. Depending on your needs, this help could be a certified hypnotist, personal trainer, or coach to instill the necessary habit changes.
Prevention should always be the primary course of action when maintaining your health, yet, seek medical advice if IR-related signs appear.
For most people avoiding insulin resistance can be prevented by implementing lifestyle changes, for example, eating a nutritious diet and routinely engaging in physical activity. In the next section, I will summarize key points on managing and preventing IR and provide resources for further information.
Summary and Resources for Further Information on Insulin Resistance
Insulin insensitivity (IR) is a condition in which cells become unresponsive to the actions of insulin, raising the possibility of type 2 diabetes and other health complications. Managing and preventing IR can be done through lifestyle changes such as diet, exercise, and supplements that may help reduce or delay its onset.
Healthy dietary choices are the most critical step in managing and preventing IR. Choosing sustenance low in immersed fat, trans fat, cholesterol, sodium, included sugars, and handled grains can help diminish the danger of creating IR. Additionally, eating plenty of fruits and vegetables will provide essential vitamins and minerals for good health. Engaging in frequent physical activity through exercise also helps preserve a healthy weight and avoid the onset of other health complications with your body.
Supplementation may also help with delaying the onset of insulin resistance. Studies have suggested that omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, could help reduce inflammation related to IR; chromium picolinate has been linked with improved glucose metabolism when taken regularly over time.
Additionally, other potential supplements include vitamin D3, magnesium citrate/oxide/malate/glycinate/aspartate/taurate; alpha lipoic acid; berberine; cinnamon extract; curcumin extract; biotin; resveratrol; quercetin dihydrate; green tea extract polyphenols EGCG & ECG; fenugreek seed powder extract 4:1; gymnema sylvestre leaf powder; banaba leaf extract 1% corosolic acid and vanadium sulfate monohydrate. However, it is important to note these are supplements to a healthy diet and not in place of one.
Consult a doctor before taking any supplement regimen if you suspect symptoms of insulin resistance or are at high risk due to family history.
FAQs in Relation to Insulin Resistance
What are the warning signs of insulin resistance?
Insulin insensitivity is when the body does not respond appropriately to insulin, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. Warning signs of insulin resistance include increased thirst and frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, weight gain or difficulty losing weight, slow wound healing, and dark patches of skin on the neck or armpits. If you experience these symptoms, you must immediately consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
How do you fix insulin resistance?
Your first step if you suspect insulin resistance is to consult your primary physician so they can run tests for you and advise on your next step. Usually, they will initially prescribe a healthy diet and exercise regime. In some instances, they may recommend medication as an additional treatment. If lifestyle changes prove difficult for you to adhere to, other professional help, such as a hypnotherapist, can help creating new habits and mental toughness required to be fully responsible for your behaviors leading to managing your blood sugar levels better.. Hypnosis can also be beneficial in decreasing stress and anxiety related to diabetes, which can have a positive effect on glucose control. Hypnosis may also bolster motivation and adherence to lifestyle modifications, such as dietary alterations and physical activity, essential for managing insulin resistance.
What is the main cause of insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance may be a result of both genetic and behavioral elements. Genetics can significantly affect how our bodies interact with insulin, while dietary habits, exercise levels, and psychological stress may contribute to insulin resistance. Medical conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or Cushing’s Syndrome may also increase insulin resistance. Ultimately, a multifaceted combination of components results in the emergence of insulin resistance.
How do I break insulin resistance quickly?
Seek your doctor for confirmation of insulin resistance and their recommendations on your best course of action. These actions will likely include changing lifestyle choices such as diet and regular exercise; for some, it could consist of medication. If you suspect difficulty adhering to any of the prescribed changes in your lifestyle, seek a certified hypnotherapist to help you implement and adhere to those changes.
How to Manage Insulin Resistance Final Points
Insulin resistance is a medical issue that can lead to adverse health effects if not dealt with quickly. Fortunately, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing insulin resistance and its associated complications. Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight are all crucial steps in preventing the development of insulin resistance. If you suspect that insulin resistance might be a concern for you or if it has already been diagnosed, your physician can offer testing and treatments to help manage the condition. By taking proactive steps now, you can protect yourself from the long-term effects of insulin resistance.
Lifestyle changes such as healthy eating habits and regular exercise can be challenging to implement, but medications have side effects, so if managing your insulin resistance is proving a struggle for you, then seek out the aid of a professional hypnotist. A hypnotherapist can teach you post-hypnotic suggestions and cues for curbing poor eating habits while encouraging a healthy diet. Hypnotherapists can help change thinking patterns which will change your eating habits.
Additional Resources Related to How to Manage Insulin Resistance:
[1] Insulin Resistance – Diabetes.org >>>
[2] What is Insulin Resistance – Very Well Health >>>
[3] Pattern Interrupt – Breaking the Habit >>>
[4] What You Need to Know About Insulin Resistance >>>
[5] Why is it So Darn Hard to Lose Weight? And Keep It Off! >>>
Library of Self-Hypnosis Downloads Products >>>
Erika Slater CH has been providing hypnosis services online and in her Mashpee MA office since 2004 and is a member of the National Guild of Hypnotists. Erika helps people ready for significant changes in their life achieve their goals and aspirations through the use of hypnosis. She frequently writes in her blog about issues around mental health and wellness. Find out more information about Erika and her services by clicking here >>>
Erika Slater CH
Free At Last Hypnosis
Massachusetts
CATEGORIES
FEATURED POSTS
Interested in making a significant change in your life and interested in learning more about what I do and how I do it? Discover my hypnotherapy services here or contact me here.

DISCOVER HOW TO START CHANGING HABITS TODAY.
In this free audio hypnosis session, you’ll experience the power of your subconscious mind to begin to change your habits. If you've never experienced hypnosis before then this is a great introduction...